一、前言
通过学习前端中实际场景的数据结构,从而加深对数据结构的理解和认识。
二、线性结构
数据结构我们可以从逻辑上分为线性结构和非线性结构。线性结构有数组,栈,链表等, 非线性结构有树,图等。
线性和非线性不代表存储结构是线性的还是非线性的。
线性结构的特点有:
- 线性结构集合中存在仅有一个的“第一个元素”
- 线性结构集合中存在仅有一个的“最后一个元素”
- 只有第一个元素没有“前驱”,别的元素都有唯一的“前驱”
- 只有最后一个元素没有“后继”,别的元素都有唯一的“后继”
有前驱和后继的就是线性数据结构。
1、数组 Array
In computer science, an array data structure, or simply an array, is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula.[1][2][3] The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array.
在计算机科学中,一个数组数据结构,或者简称一个数组,是一个由元素集合(值或变量)组成的数据结构,每个元素由至少一个数组索引或键来标识。一个被存储的数组中的每个元素的位置都可以通过一个数学公式从它的索引元组中计算出来。最简单的数据结构类型是一个线性数组,也称为一维数组。
数组是最古老和最重要的数据结构之一,几乎每个程序都会使用它。它还被用来实现许多其他的数据结构,比如列表和字符串。数组有效地利用了计算机的寻址逻辑addressing logic of computers。在大多数现代计算机和许多外部存储设备中,内存是一个一维的word数组,其索引是它们的地址。
处理器,尤其是向量处理器,通常是针对数组操作进行优化的。
数组通常被用来表示数组数据类型,这是一种由大多数高级编程语言提供的数据类型,它由一组值或变量组成,这些值或变量可以由一个或多个在运行时计算的索引来选择。数组类型通常由数组结构来实现;然而,在某些语言中,它们可能是由哈希表、链表、搜索树或其他数据结构实现的。
JavaScript 中, JSArray 继承自 JSObject ,或者说它就是一个特殊的对象,内部是以 key-value 形式存储数据,所以 JavaScript 中的数组可以存放不同类型的值。它有两种存储方式,快数组与慢数组,初始化空数组时,使用快数组,快数组使用连续的内存空间,当数组长度达到最大时,JSArray 会进行动态的扩容,以存储更多的元素,相对慢数组,性能要好得多。当数组中 hole 太多时,会转变成慢数组,即以哈希表的方式( key-value 的形式)存储数据,以节省内存空间。
特性
-
存储在物理结构上是连续的。数组所占用的内存空间必须是连续的,不能由两个或多个内存碎片存储。
-
底层的数组长度是不可变的。为什么说是底层的数组?因为JavaScript这类特殊的语言,像Java、Python等语言中声明数组时必须指定数组的长度,并且指定长度之后长度不可变化,如果对超过数组长度的内存进行操作会发生数组越界异常;而JavaScript中在声明数组时可以不指定数组长度,并且可以随意操作数组(添加、删除),原因是js引擎在数组长度不够时进行了数组扩容。
数组扩容:当数组长度不够用需要扩容时,此时需要系统重新分配一块扩容后长度的物理空间,然后将扩容前的数组元素复制到新的物理空间中,这个过程是消耗性能的。尤其是在数据量较大时,所以尽可能避免发生数组扩容。
- 数组的变量指向了数组的第一个元素。比如声明一个数组
arr,那么arr其实指向的是数组的第一项的内存地址,由于在内存中数组是连续的,可以通过数组的第一项来访问整个数组中的所有元素。
优点
- 查询性能好,在查询某个位置的元素时尤为明显,由于数组在内存地址中是连续的,并且我们通过
arr[2]访问数组中的某个元素时,arr[n]其中的n其实为内存地址的偏移量,在操作系统中通过偏移量来进行查询效率是最高的。
对于一个数组,访问a[3]和a[1000]的时间复杂度都是一样的:其都是先找到数组的开头指针,即a[0]的指针,然后用该指针+3或者加1000,就可以计算出对应的指针位置。
查找
根据下标随机访问的时间复杂度为 O(1);
插入或删除
时间复杂度为 O(n);
js数组可以保存不同类型值
// The JSArray describes JavaScript Arrays
// Such an array can be in one of two modes:
// - fast, backing storage is a FixedArray and length <= elements.length();
// Please note: push and pop can be used to grow and shrink the array.
// - slow, backing storage is a HashTable with numbers as keys.
class JSArray: public JSObject {
public:
// [length]: The length property.
DECL_ACCESSORS(length, Object)
// ...
// Number of element slots to pre-allocate for an empty array.
static const int kPreallocatedArrayElements = 4;
};
JSArray 是继承自 JSObject 的,所以在 JavaScript 中,数组可以是一个特殊的对象,内部也是以 key-value 形式存储数据,所以 JavaScript 中的数组可以存放不同类型的值(因为对象可以保存不同类型的值)。
从注释上看,它有两种存储方式:
- fast:存储结构是
FixedArray,并且数组长度<= elements.length(),push或pop时可能会伴随着动态扩容或减容 - slow:存储结构是
HashTable(哈希表),并且数组下标作为key
fast 模式下数组在源码里面叫 FastElements ,而 slow 模式下的叫做 SlowElements 。
1. 快数组(FastElements)
FixedArray 是 V8 实现的一个类似于数组的类,它表示一段连续的内存,可以使用索引直接定位。新创建的空数组默认就是快数组。当数组满(数组的长度达到数组在内存中申请的内存容量最大值)的时候,继续 push 时, JSArray 会进行动态的扩容,以存储更多的元素。
2. 慢数组(SlowElements)
慢数组以哈希表的形式存储在内存空间里,它不需要开辟连续的存储空间,但需要额外维护一个哈希表,与快数组相比,性能相对较差。
// src/objects/dictionary.h
class EXPORT_TEMPLATE_DECLARE(V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE) Dictionary
: public HashTable<Derived, Shape> {
using DerivedHashTable = HashTable<Derived, Shape>;
public:
using Key = typename Shape::Key;
// Returns the value at entry.
inline Object ValueAt(InternalIndex entry);
inline Object ValueAt(const Isolate* isolate, InternalIndex entry);
// ...
};
内部是一个 HashTable.
3. fast和slow互转
**①. fast => slow **
// src/objects/js-objects.h
static const uint32_t kMaxGap = 1024;
// src/objects/dictionary.h
// JSObjects prefer dictionary elements if the dictionary saves this much
// memory compared to a fast elements backing store.
static const uint32_t kPreferFastElementsSizeFactor = 3;
// src/objects/js-objects-inl.h
// If the fast-case backing storage takes up much more memory than a dictionary
// backing storage would, the object should have slow elements.
// static
static inline bool ShouldConvertToSlowElements(uint32_t used_elements,
uint32_t new_capacity) {
uint32_t size_threshold = NumberDictionary::kPreferFastElementsSizeFactor *
NumberDictionary::ComputeCapacity(used_elements) *
NumberDictionary::kEntrySize;
// 快数组新容量是扩容后的容量3倍之多时,也会被转成慢数组
return size_threshold <= new_capacity;
}
static inline bool ShouldConvertToSlowElements(JSObject object,
uint32_t capacity,
uint32_t index,
uint32_t* new_capacity) {
STATIC_ASSERT(JSObject::kMaxUncheckedOldFastElementsLength <=
JSObject::kMaxUncheckedFastElementsLength);
if (index < capacity) {
*new_capacity = capacity;
return false;
}
// 当加入的索引值(例如例3中的2000)比当前容量capacity 大于等于 1024时,
// 返回true,转为慢数组
if (index - capacity >= JSObject::kMaxGap) return true;
*new_capacity = JSObject::NewElementsCapacity(index + 1);
DCHECK_LT(index, *new_capacity);
// TODO(ulan): Check if it works with young large objects.
if (*new_capacity <= JSObject::kMaxUncheckedOldFastElementsLength ||
(*new_capacity <= JSObject::kMaxUncheckedFastElementsLength &&
ObjectInYoungGeneration(object))) {
return false;
}
return ShouldConvertToSlowElements(object.GetFastElementsUsage(),
*new_capacity);
}
所以,当处于以下情况时,快数组会被转变为慢数组:
- 当加入的索引值 index 比当前的容量 capacity 差值大于等于 1024 时(index - capacity >= 1024)
- 快数组新容量是扩容后的容量 3 倍之多时
例如:向快数组里增加一个大索引同类型值
var arr = [1, 2, 3]
arr[2000] = 10;
当往 arr 增加一个 2000 的索引时,arr 被转成慢数组。节省了大量的内存空间(从索引为 2 到索引为 2000)。
②. slow => fast
static bool ShouldConvertToFastElements(JSObject object,
NumberDictionary dictionary,
uint32_t index,
uint32_t* new_capacity) {
// If properties with non-standard attributes or accessors were added, we
// cannot go back to fast elements.
if (dictionary.requires_slow_elements()) return false;
// Adding a property with this index will require slow elements.
if (index >= static_cast<uint32_t>(Smi::kMaxValue)) return false;
if (object.IsJSArray()) {
Object length = JSArray::cast(object).length();
if (!length.IsSmi()) return false;
*new_capacity = static_cast<uint32_t>(Smi::ToInt(length));
} else if (object.IsJSArgumentsObject()) {
return false;
} else {
*new_capacity = dictionary.max_number_key() + 1;
}
*new_capacity = Max(index + 1, *new_capacity);
uint32_t dictionary_size = static_cast<uint32_t>(dictionary.Capacity()) *
NumberDictionary::kEntrySize;
// Turn fast if the dictionary only saves 50% space.
return 2 * dictionary_size >= *new_capacity;
}
当慢数组的元素可存放在快数组中且长度在 smi 之间且仅节省了50%的空间,则会转变为快数组
js数组的动态扩容与减容(FastElements)
默认空数组初始化大小为 4 :
// Number of element slots to pre-allocate for an empty array.
static const int kPreallocatedArrayElements = 4;
在 JavaScript 中,当数组执行 push 操作时,一旦发现数组内存不足,将进行扩容。
在 Chrome 源码中, push 的操作是用汇编实现的,在 c++ 里嵌入的汇编,以提高执行效率,并且在汇编的基础上用 c++ 封装了一层,在编译执行的时候,会将这些 c++ 代码转成汇编代码。
计算新容量的函数:
// js-objects.h
static const uint32_t kMinAddedElementsCapacity = 16;
// code-stub-assembler.cc
Node* CodeStubAssembler::CalculateNewElementsCapacity(Node* old_capacity,
ParameterMode mode) {
CSA_SLOW_ASSERT(this, MatchesParameterMode(old_capacity, mode));
Node* half_old_capacity = WordOrSmiShr(old_capacity, 1, mode);
Node* new_capacity = IntPtrOrSmiAdd(half_old_capacity, old_capacity, mode);
Node* padding =
IntPtrOrSmiConstant(JSObject::kMinAddedElementsCapacity, mode);
return IntPtrOrSmiAdd(new_capacity, padding, mode);
}
所以扩容后新容量计公式为:
new_capacity = old_capacity / 2 + old_capacity + 16
即老的容量的 1.5 倍加上 16 。初始化为 4 个,当 push 第 5 个的时候,容量将会变成:
new_capacity = 4 / 2 + 4 + 16 = 22
接着申请一块这么大的内存,把老的数据拷过去,把新元素放在当前 length 位置,然后将数组的 length + 1,并返回 length。
所以,扩容可以分为以下几步:
push操作时,发现数组内存不足- 申请 new_capacity = old_capacity /2 + old_capacity + 16 那么长度的内存空间
- 将数组拷贝到新内存中
- 把新元素放在当前 length 位置
- 数组的 length + 1
- 返回 length
整个过程,用户是无感知的,不像 C,需用用户手动申请内存空间。
当数组执行 pop 操作时,会判断 pop 后数组的容量,是否需要进行减容。
不同于数组的 push 使用汇编实现的, pop 使用 c++ 实现的。
判断是否进行减容:
if (2 * length <= capacity) {
// If more than half the elements won't be used, trim the array.
isolate->heap()->RightTrimFixedArray(*backing_store, capacity - length);
} else {
// Otherwise, fill the unused tail with holes.
BackingStore::cast(*backing_store)->FillWithHoles(length, old_length);
}
所以,当数组 pop 后,如果数组容量大于等于 length 的 2 倍,则进行容量调整,使用 RightTrimFixedArray 函数,计算出需要释放的空间大小,做好标记,等待 GC 回收;如果数组容量小于 length 的 2 倍,则用 holes 对象填充。
所以,减容可以分为以下几步:
pop操作时,获取数组length- 获取
length - 1上的元素(要删除的元素) - 数组
length - 1 - 判断数组的总容量是否大于等于 length - 1 的 2 倍
- 是的话,使用
RightTrimFixedArray函数,计算出需要释放的空间大小,并做好标记,等待GC回收 - 不是的话,用
holes对象填充 - 返回要删除的元素
2、队列
In computer science, a queue is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence. By convention, the end of the sequence at which elements are added is called the back, tail, or rear of the queue, and the end at which elements are removed is called the head or front of the queue, analogously to the words used when people line up to wait for goods or services.
The operation of adding an element to the rear of the queue is known as enqueue, and the operation of removing an element from the front is known as dequeue. Other operations may also be allowed, often including a peek or front operation that returns the value of the next element to be dequeued without dequeuing it.
The operations of a queue make it a first-in-first-out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. This is equivalent to the requirement that once a new element is added, all elements that were added before have to be removed before the new element can be removed. A queue is an example of a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection. Queues are common in computer programs, where they are implemented as data structures coupled with access routines, as an abstract data structure or in object-oriented languages as classes. Common implementations are circular buffers and linked lists.
队列是一种受限的序列。受限在哪呢?受限就受限在它只能够操作队尾和队首,并且只能只能在队尾添加元素,在队首删除元素。而数组就没有这个限制。
在计算机科学中,一个 队列 (queue) 是一种特殊类型的抽象数据类型或集合,集合中的实体按顺序保存。
队列基本操作有两种:
- 向队列的后端位置添加实体,称为入队
- 从队列的前端位置移除实体,称为出队。
队列中元素先进先出 FIFO (first in, first out) 的示意
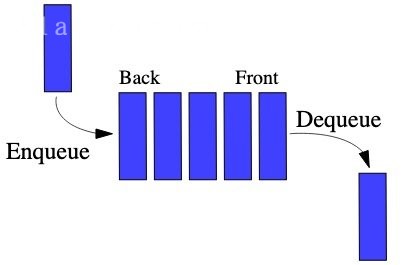
当然,也可以把队列看做是一个单向通道,先进去的元素,必定会先出来(不考虑优先级的情况下)FIFO first-in-first-out,队列的元素从队尾进入,从队头出来。
队列可以看做是一个单向通道,先进去的元素,必定会先出来(不考虑优先级的情况下)FIFO first-in-first-out,队列的元素从队尾进入,从队头出来。
抽象队列的数据结构类型
-
size(属性):队列中的元素个数
-
dataSource(属性):队列中存储元素的数组
-
enqueue(方法):向队尾添加一个元素
-
dequeue(方法):删除队头元素
-
front(方法):读取队头元素
-
back(方法):读取队尾元素
-
length(方法):返回队列元素个数
-
clear(方法):清空队列
-
empty(方法):判断队列是否为空
-
toString(方法):显示所有的队列元素
有了队列的抽象数据结构类型,我们可以得到一下的队列类:
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.dataSource = [];
this.size = 0;
}
// enqueue:向队列尾增加元素
enqueue(element) {
this.dataSource.push(element);
this.size++;
}
// dequeue: 删除队头元素
dequeue() {
if (this.empty()) {
this.size--;
return this.dataSource.shift();
}
}
// empty: 判断是否为空队列
empty() {
if (this.size > 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// front: 返回队头元素
front() {
if (this.empty()) {
return this.dataSource[0];
}
}
// back: 返回队尾元素
back() {
if (this.empty()) {
return this.dataSource[this.size - 1];
}
}
// length: 返回队列元素总数
length() {
return this.size;
}
// clear: 清空队列
clear() {
this.dataSource.length = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
// toString: 返回队列所有元素
toString() {
return this.dataSource;
}
}
3、栈
The order in which elements come off a stack gives rise to its alternative name, LIFO (last in, first out). Additionally, a peek operation may give access to the top without modifying the stack.[1] The name "stack" for this type of structure comes from the analogy to a set of physical items stacked on top of each other. This structure makes it easy to take an item off the top of the stack, while getting to an item deeper in the stack may require taking off multiple other items first.[2]
Considered as a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection, the push and pop operations occur only at one end of the structure, referred to as the top of the stack. This data structure makes it possible to implement a stack as a singly linked list and a pointer to the top element. A stack may be implemented to have a bounded capacity. If the stack is full and does not contain enough space to accept an entity to be pushed, the stack is then considered to be in an overflow state. The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack.
栈也是一种受限的序列,它受限就受限在只能够操作栈顶,不管入栈还是出栈,都是在栈顶操作。同样地,数组就没有这个限制。
在计算机科学中,一个栈 (stack) 是一种抽象数据类型,用作表示元素的集合,具有两种主要操作:
- push, 添加元素到栈的顶端(末尾)
- pop, 移除栈最顶端(末尾)的元素
以上两种操作可以简单概括为后进先出 (LIFO = last in, first out)。
此外,应有一个 peek 操作用于访问栈当前顶端(末尾)的元素。(只返回不弹出)
"栈"这个名称,可类比于一组物体的堆叠(一摞书,一摞盘子之类的)。
栈的 push 和 pop 操作的示意图:
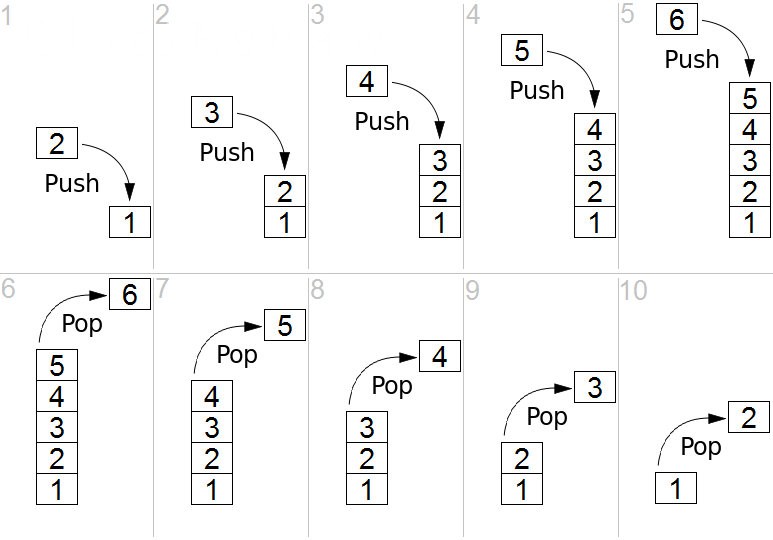
你可以这样理解,栈就是一个装水的水桶,我们要取水的话只能从水桶的最上面取水,最先倒入水桶的水,是最后取出来的。
所以栈就是一种特殊的列表,栈内的元素只能通过列表的一端进行访问,这一端称为栈顶。栈被称为一种后入先出(LIFO,last-in-first-out)的数据结构。
我们来抽象一下栈的数据类型结构
-
dataSource (属性):用于存储栈的元素
-
size(属性):栈内元素的个数
-
clear(方法):清除所有的栈内元素
-
push(方法):向栈内添加元素
-
pop(方法):删除当前栈顶元素
-
peek(方法):显示当前栈顶元素
-
length(方法):返回栈内元素个数
根据上面的抽象定义我们得到栈类Stack
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.dataSource = [];
this.size = 0;
}
// clear: 清除所有元素
clear() {
this.dataSource.length = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
// push:添加新元素
push(element) {
this.dataSource[this.size++] = element;
}
// pop: 删除栈顶元素
pop() {
if (this.size > 0) {
return this.dataSource.splice(--this.size, 1);
}
return false;
}
//peek: 返回当前栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.size > 0) {
return this.dataSource[this.size -1];
}
}
// length: 返回当前栈内元素个数
length() {
return this.size;
}
}
我们根据这个栈类来实现一个判断字符串是否是回文的函数(如果一个字符串从左到右和从右到左是相等的话,那么这个字符串就是回文,例如‘aabbaa’)
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.dataSource = [];
this.size = 0;
}
// clear: 清除所有元素
clear() {
this.dataSource.length = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
// push:添加新元素
push(element) {
this.dataSource[this.size++] = element;
}
// pop: 删除栈顶元素
pop() {
if (this.size > 0) {
return this.dataSource.splice(--this.size, 1)[0];
}
return false;
}
//peek: 返回当前栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.size > 0) {
return this.dataSource[this.size - 1];
}
}
// length: 返回当前栈内元素个数
length() {
return this.size;
}
}
const str1 = 'aabbaa';
const str2 = 'aabbcc';
isPalindrome(str1);
isPalindrome(str2);
function isPalindrome(str) {
const strArr = str.split('');
const stack = new Stack();
let newStr = '';
while (strArr.length) {
stack.push(strArr.splice(0, 1)[0]);
}
while (stack.length()) {
newStr += stack.pop();
}
console.log(newStr);
if (newStr === str) {
console.log(str + ':是回文');
}
else console.log(str + ':不是是回文');
}
链表
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence. In its most basic form, each node contains: data, and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing more efficient insertion or removal of nodes at arbitrary positions. A drawback of linked lists is that access time is linear (and difficult to pipeline). Faster access, such as random access, is not feasible. Arrays have better cache locality compared to linked lists.
引用自维基百科 Linked list.
各种数据结构,不管是队列,栈等线性数据结构还是树,图的等非线性数据结构,从根本上底层都是数组和链表。
不管你用的是数组还是链表,用的都是计算机内存,物理内存是一个个大小相同的内存单元构成的,如图:
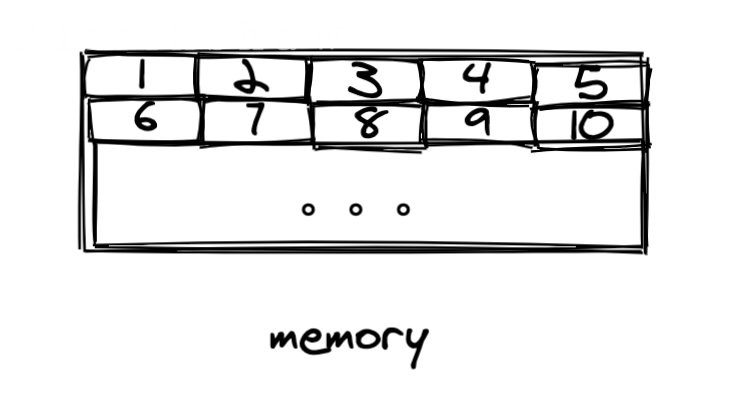
而数组和链表虽然用的都是物理内存,都是两者在对物理的使用上是非常不一样的,如图:
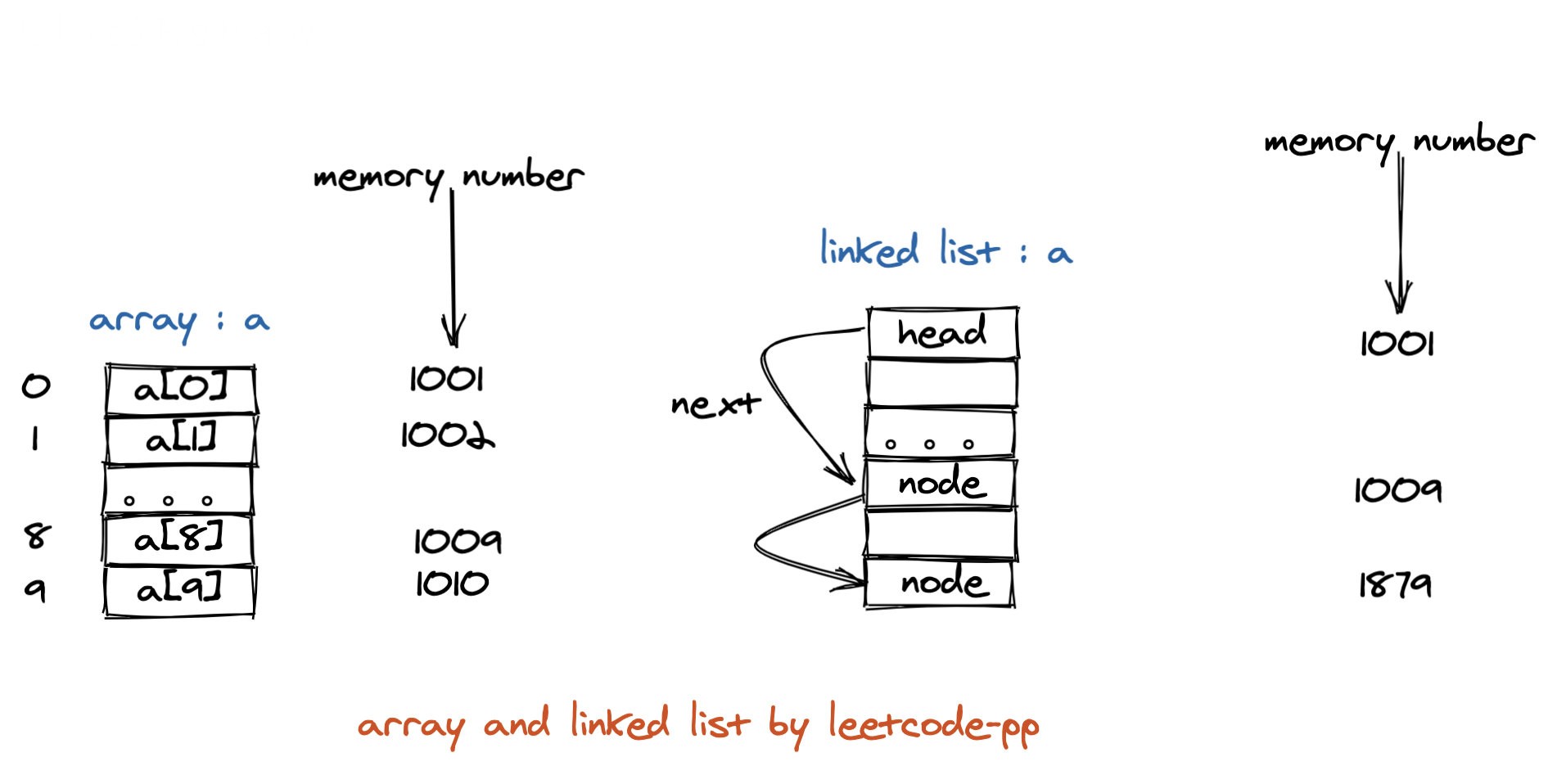
从物理上来说,即在内存中,这两种逻辑结构所对应的物理存储分布上看,数组占用的是一块连续的内存区,而链表在内存中,是分散的,因为是分散的,就需要一种东西把他们串起来,这样才能形成逻辑上的线性表,不像数组,与生俱来具有“线性”的成分。因为链表比数组多了一个“串起来”的额外操作,这个操作就是加了个指向下个节点的指针,所以对于链表来说,存储一个节点,所要消耗的资源就多了。也正因为这种物理结构上的差异,导致了他们在访问、增加、删除节点这三种操作上所带来的时间复杂度不同。
注意,这里的链表是不一定连续,而不是一定不连续。
一般我们是通过一个叫 next 指针来遍历查找。链表其实就是一个结构体。 比如一个可能的单链表的定义可以是:
interface ListNode<T> {
data: T;
next: ListNode<T>;
}
data 是数据域,存放数据,next 是一个指向下一个节点的指针。
在图中可看出,数组所占据的是一块连续的空间,这样的数据结构对于新增和删除是极其不友好的,这样大概率会触发动态扩容;对数组头部的插入和删除时间复杂度都是$O(N)$,而平均复杂度也是$O(N)$,只有对尾部的插入和删除才是$O(1)$。
在平时排队中,如果有人插队,在插队的前方的人是不受影响的,但是后面的人全部受影响。如果这个插队的人跑到最前面去了,那所有人都有意见了。而且考虑在内存上,不是所有时候都有机会往后顺延的,碰到原来的空间不够,是整个派对的队伍都要换位置的,这就惨了。
简单来说”数组对查询特别友好,对删除和添加不友好“。
为了解决这个问题,就有了链表。
链表只有一个后驱节点 next,如果是双向链表还会有一个前驱节点 pre。
有没有想过为啥只有二叉树,而没有一叉树。实际上链表就是特殊的树,即一叉树。
链表的插入只需要考虑要插入位置前驱节点和后继节点,对于其他位置都是不会有影响的。因此在给定指针的情况下插入的操作时间复杂度为O(1)。这里给定指针中的指针指的是插入位置的前驱节点。
如果没有给定指针,我们需要先遍历找到节点,因此最坏情况下时间复杂度为 O(N)。




